from ribasim import run_ribasimReservoir
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
from ribasim import Model, Node
from ribasim.nodes import (
basin,
flow_boundary,
tabulated_rating_curve,
user_demand,
)
from shapely.geometry import Pointbase_dir = Path("crystal-basin")
starttime = "2022-01-01"
endtime = "2023-01-01"
model = Model(
starttime=starttime,
endtime=endtime,
crs="EPSG:4326",
)These nodes are identical to the previous tutorial:
# FlowBoundary
data = pd.DataFrame({
"time": pd.date_range(start="2022-01-01", end="2023-01-01", freq="MS"),
"main": [74.7, 57.9, 63.2, 183.9, 91.8, 47.5, 32.6, 27.6, 26.5, 25.1, 39.3, 37.8, 57.9],
"minor": [16.3, 3.8, 3.0, 37.6, 18.2, 11.1, 12.9, 12.2, 11.2, 10.8, 15.1, 14.3, 11.8]
}) # fmt: skip
data["total"] = data["minor"] + data["main"]
main = model.flow_boundary.add(
Node(1, Point(0.0, 0.0), name="main"),
[
flow_boundary.Time(
time=data.time,
flow_rate=data.main,
)
],
)
minor = model.flow_boundary.add(
Node(2, Point(-3.0, 0.0), name="minor"),
[
flow_boundary.Time(
time=data.time,
flow_rate=data.minor,
)
],
)
# Basin
confluence = model.basin.add(
Node(3, Point(-1.5, -1), name="confluence"),
[
basin.Profile(area=[672000, 5600000], level=[0, 6]),
basin.State(level=[4]),
basin.Time(time=[starttime, endtime]),
],
)
# TabulatedRatingCurve
weir = model.tabulated_rating_curve.add(
Node(4, Point(-1.5, -1.5), name="weir"),
[
tabulated_rating_curve.Static(
level=[0.0, 2, 5],
flow_rate=[0.0, 50, 200],
)
],
)
diversion_weir = model.tabulated_rating_curve.add(
Node(8, Point(-1.125, -0.75), name="diversion_weir"),
[
tabulated_rating_curve.Static(
level=[0.0, 1.5, 5],
flow_rate=[0.0, 45, 200],
)
],
)
# UserDemand
irrigation = model.user_demand.add(
Node(7, Point(-1.5, 0.5), name="irrigation"),
[
user_demand.Time(
demand=[0.0, 0.0, 10, 12, 12, 0.0],
return_factor=0,
min_level=0,
demand_priority=1,
time=[
starttime,
"2022-03-31",
"2022-04-01",
"2022-07-01",
"2022-09-30",
"2022-10-01",
],
)
],
)
# Terminal
sea = model.terminal.add(Node(5, Point(-1.5, -3.0), name="sea"))Due to the increase of population and climate change Crystal city has implemented a reservoir upstream to store water for domestic use (See Figure 1). The reservoir is to help ensure a reliable supply during dry periods. In this module, the user will update the model to incorporate the reservoir’s impact on the whole Crystal basin.

1 Reservoir
1.1 Add a Basin
The diversion_basin from the previous tutorial is not used, but replaced by a larger reservoir Basin. Its water will play an important role for the users (the city and the irrigation district). The reservoir has a maximum area of \(32.3 \text{ km}^2\) and a maximum depth of \(7 \text{ m}\).
reservoir = model.basin.add(
Node(6, Point(-0.75, -0.5), name="reservoir"),
[
basin.Profile(area=[20000000, 32300000], level=[0, 7]),
basin.State(level=[3.5]),
basin.Time(time=[starttime, endtime]),
],
)1.2 Add a demand node
\(50.000\) people live in Crystal City. To represents the total flow rate or abstraction rate required to meet the water demand of \(50.000\) people, another demand node needs to be added assuming a return flow of \(60\%\).
city = model.user_demand.add(
Node(9, Point(0, -1), name="city"),
[
user_demand.Time(
# Total demand in m³/s
demand=[0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.10, 0.12, 0.14, 0.15, 0.14, 0.12, 0.10, 0.09, 0.08],
return_factor=0.6,
min_level=0,
demand_priority=1,
time=pd.date_range(start="2022-01-01", periods=12, freq="MS"),
)
],
) # fmt: skipmodel.link.add(main, reservoir, name="main")
model.link.add(minor, confluence, name="minor")
model.link.add(reservoir, irrigation, name="irrigation")
model.link.add(irrigation, confluence)
model.link.add(reservoir, city, name="city")
model.link.add(city, confluence, name="city returnflow")
model.link.add(reservoir, diversion_weir, name="not diverted")
model.link.add(diversion_weir, confluence)
model.link.add(confluence, weir)
model.link.add(weir, sea, name="sea")model.plot();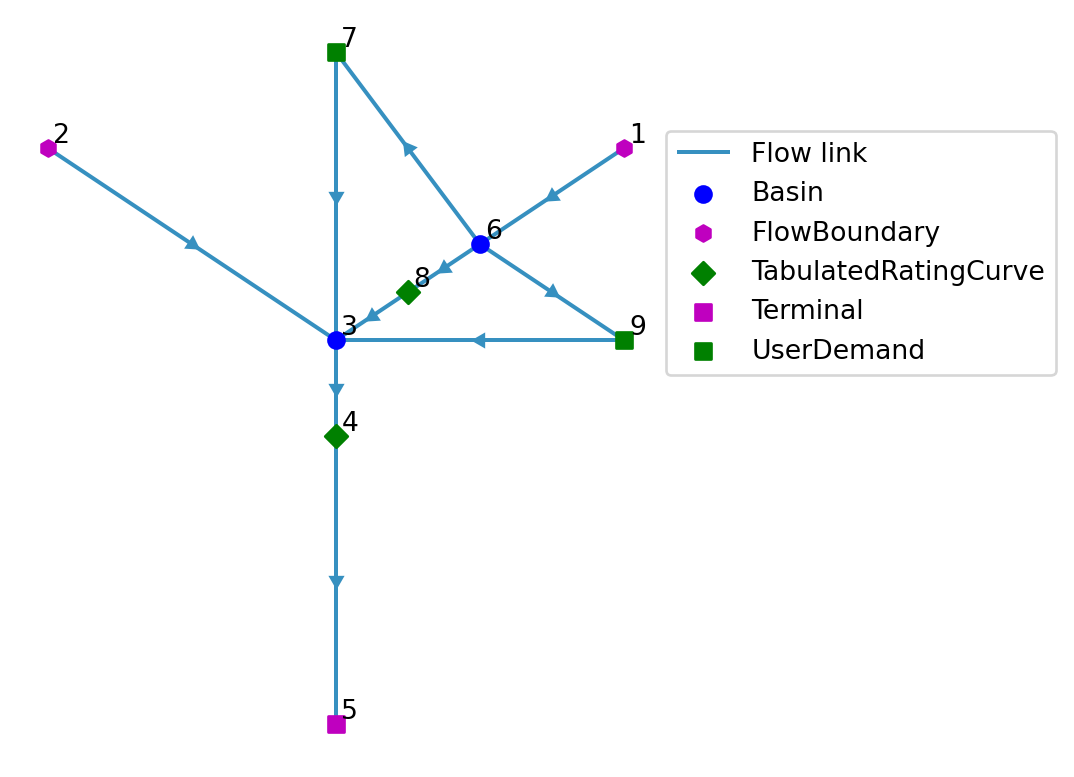
toml_path = base_dir / "Crystal-3/ribasim.toml"
model.write(toml_path)PosixPath('crystal-basin/Crystal-3/ribasim.toml')1.3 Adjust the code
Adjust the naming of the Basin in the dictionary mapping and the saving file should be Crystal-3.
run_ribasim(toml_path)┌ Info: Starting a Ribasim simulation.
│ toml_path = "crystal-basin/Crystal-3/ribasim.toml"
│ cli.ribasim_version = "2025.6.0"
│ starttime = 2022-01-01T00:00:00
│ endtime = 2023-01-01T00:00:00
└ threads = 1
Simulating 0%| | ETA: N/A
Simulating 0%| | ETA: 18:49:44
Simulating 6%|██▎ | ETA: 0:09:56
Simulating 9%|███▍ | ETA: 0:06:19
Simulating 14%|█████▊ | ETA: 0:03:33
Simulating 18%|███████ | ETA: 0:02:46
Simulating 25%|█████████▉ | ETA: 0:01:48
Simulating 25%|█████████▉ | ETA: 0:01:48
Simulating 25%|█████████▉ | ETA: 0:01:48
Simulating 25%|█████████▉ | ETA: 0:01:48
Simulating 27%|██████████▊ | ETA: 0:01:36
Simulating 32%|████████████▉ | ETA: 0:01:14
Simulating 34%|█████████████▊ | ETA: 0:01:07
Simulating 41%|████████████████▎ | ETA: 0:00:52
Simulating 44%|█████████████████▋ | ETA: 0:00:45
Simulating 50%|███████████████████▉ | ETA: 0:00:36
Simulating 53%|█████████████████████ | ETA: 0:00:32
Simulating 58%|███████████████████████▎ | ETA: 0:00:26
Simulating 63%|█████████████████████████▎ | ETA: 0:00:21
Simulating 68%|███████████████████████████▍ | ETA: 0:00:16
Simulating 75%|█████████████████████████████▉ | ETA: 0:00:12
Simulating 79%|███████████████████████████████▍ | ETA: 0:00:10
Simulating 83%|█████████████████████████████████▍ | ETA: 0:00:07
Simulating 88%|███████████████████████████████████▍ | ETA: 0:00:05
Simulating 92%|████████████████████████████████████▉ | ETA: 0:00:03
Simulating 100%|████████████████████████████████████████| Time: 0:00:35
[ Info: Computation time: 16 seconds, 564 milliseconds
[ Info: The model finished successfully.2 Plot reservoir storage and level
df_basin = pd.read_feather(base_dir / "Crystal-3/results/basin.arrow")
# Create pivot tables and plot for Basin data
df_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(
index="time", columns="node_id", values=["storage", "level"]
)
df_basin_wide = df_basin_wide.loc[:, pd.IndexSlice[:, reservoir.node_id]]
# Plot level and storage on the same graph with dual y-axes
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
# Plot level on the primary y-axis
color = "b"
ax1.set_xlabel("Time")
ax1.set_ylabel("Level [m]", color=color)
ax1.plot(df_basin_wide.index, df_basin_wide["level"], color=color)
ax1.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=color)
# Create a secondary y-axis for storage
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
color = "r"
ax2.set_ylabel("Storage [m³]", color="r")
ax2.plot(df_basin_wide.index, df_basin_wide["storage"], linestyle="--", color=color)
ax2.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=color)
fig.tight_layout() # Adjust layout to fit labels
plt.title("Basin level and storage")
plt.show()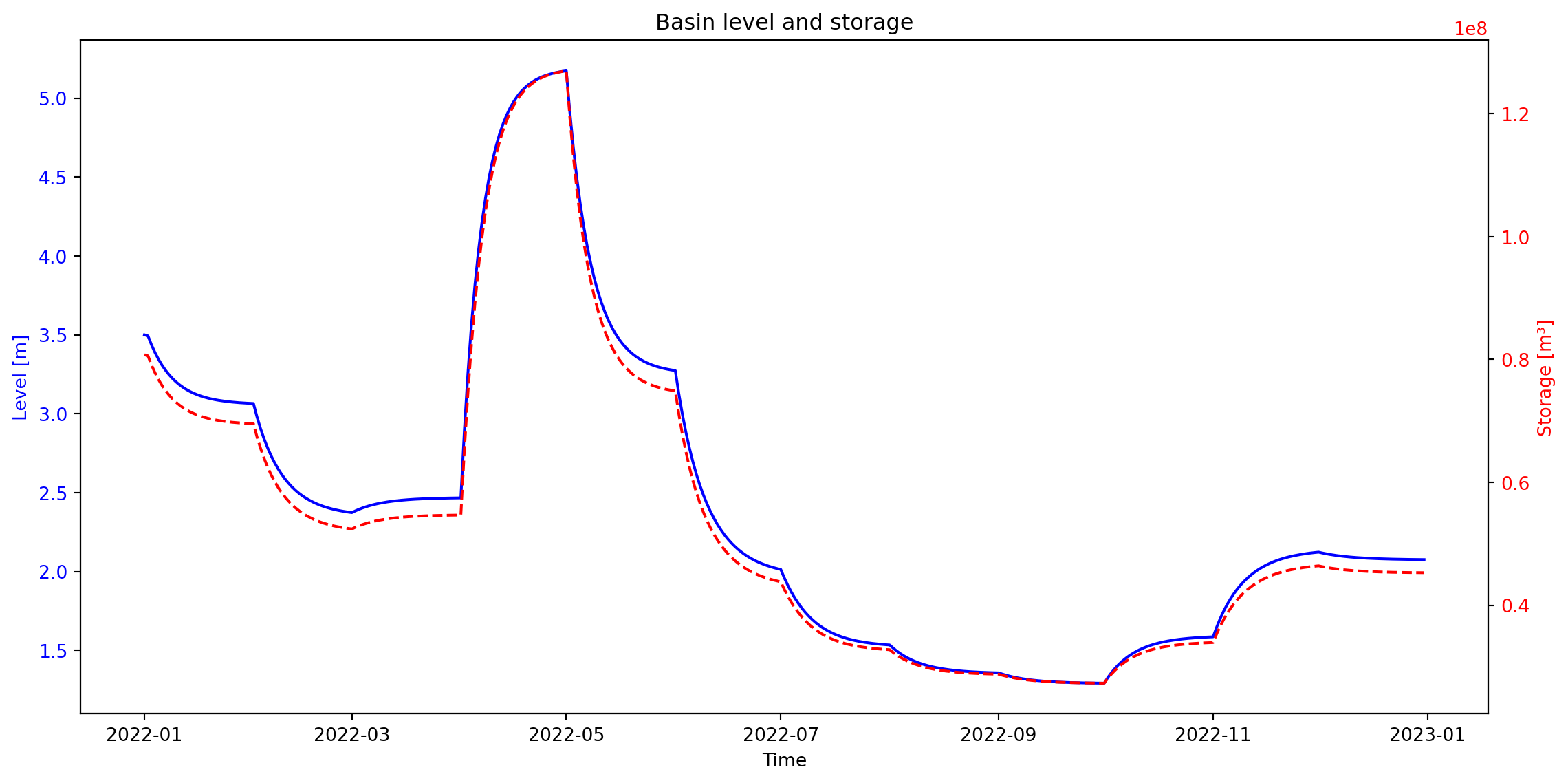
The figure above illustrates the storage and water level at the reservoir. As expected, after increasing the profile of the Basin, its storage capacity increased as well.
3 Plot flows
df_flow = pd.read_feather(base_dir / "Crystal-3/results/flow.arrow")
# Add the link names and then remove unnamed links
df_flow["name"] = model.link.df["name"].loc[df_flow["link_id"]].to_numpy()
df_flow = df_flow[df_flow["name"].astype(bool)]
# Plot the flow data, interactive plot with Plotly
pivot_flow = df_flow.pivot_table(
index="time", columns="name", values="flow_rate"
).reset_index()
fig = px.line(pivot_flow, x="time", y=pivot_flow.columns[1:], title="Flow [m3/s]")
fig.update_layout(legend_title_text="Link")
fig.show()